Tilrettelegg for effektiv input
Skrevet av: Morten Tollefsen
Det å tilrettelegge for forståelig og effektiv input innebærer blant annet:
- Gode ledetekster (label)
- Forståelige forklaringer hvis ledetekster ikke strekker til
- Merking av frivillige og obligatoriske felt
- Bruke kjente kontroller
I denne artikkelen vil jeg legge vekt på tekniske grep som kan gjøre input så effektivt som mulig. Mer spesifikt bruk av attributtene autocomplete, type og inputmode. Jeg har brukt tastatureksempler fra iPhone, men dette er veldig sammenliknbart med Android. Hvis du viser artikkelen med mobil kan du gå inn i et felt for å sjekke hvilket tastatur som vises.
Suksesskriterie 1.3.5
Identifiser formål med inndata i WCAG sier litt forenklet at vi skal merke formålet
med felt. Slik merking kan hjelpe personer med kognitive funksjonsnedsettelser,
eksempelvis ved å benytte ikoner som sier hva som forventes i et felt. I HTML er
autocomplete-attributtet det vi kan benytte, og det er jo faktisk "bra for alle" å slippe og
skrive inn alt.
Merk: det kan finnes personvernhensyn som forhindrer bruk av autocomplete, men dette
problematiseres ikke i denne artikkelen.
autocomplete-attributtet
Autocomplete spesifiserer om et skjema eller et inndatafelt skal ha autofullføring på eller av. Autofullføring lar nettleseren forutsi verdien. Når en bruker begynner å skrive i et felt, skal nettleseren vise alternativer for å fylle ut feltet, basert på tidligere innskrevne verdier. Det er mulig å ha autofullføring "på" for skjemaet, og "av" for spesifikke inndatafelt, eller omvendt.
Autocomplete fungerer med følgende input-typer: text, search, url, tel, email, password, datepickers, range, og color. Attributtet skal brukes for innsamling av personlige data. Eks: brukerens epost, men ikke epost til brukerens ektefelle.
autocomplete-verdier
- "
off" -
The browser is not permitted to automatically enter or select a value for this field. It is possible that the document or application provides its own autocomplete feature, or that security concerns require that the field's value not be automatically entered.
Note: In most modern browsers, setting
autocompleteto "off" will not prevent a password manager from asking the user if they would like to save username and password information, or from automatically filling in those values in a site's login form. See the autocomplete attribute and login fields. - "
on" -
The browser is allowed to automatically complete the input. No guidance is provided as to the type of data expected in the field, so the browser may use its own judgement.
- "
name" -
The field expects the value to be a person's full name. Using "
name" rather than breaking the name down into its components is generally preferred because it avoids dealing with the wide diversity of human names and how they are structured; however, you can use the followingautocompletevalues if you do need to break the name down into its components: - "
honorific-prefix" -
The prefix or title, such as "Mrs.", "Mr.", "Miss", "Ms.", "Dr.", or "Mlle.".
- "
given-name" -
The given (or "first") name.
- "
additional-name" -
The middle name.
- "
family-name" -
The family (or "last") name.
- "
honorific-suffix" -
The suffix, such as "Jr.", "B.Sc.", "PhD.", "MBASW", or "IV".
- "
nickname" -
A nickname or handle.
- "
email" -
An email address.
- "
username" -
A username or account name.
- "
new-password" -
A new password. When creating a new account or changing passwords, this should be used for an "Enter your new password" or "Confirm new password" field, as opposed to a general "Enter your current password" field that might be present. This may be used by the browser both to avoid accidentally filling in an existing password and to offer assistance in creating a secure password (see also Preventing autofilling with autocomplete="new-password").
- "
current-password" -
The user's current password.
- "
one-time-code" -
A one-time password (OTP) for verifying user identity that is used as an additional factor in a sign-in flow. Most commonly this is a code received via some out-of-channel mechanism, such as SMS, email, or authenticator application.
- "
organization-title" -
A job title, or the title a person has within an organization, such as "Senior Technical Writer", "President", or "Assistant Troop Leader".
- "
organization" -
A company or organization name, such as "Acme Widget Company" or "Girl Scouts of America".
- "
street-address" -
A street address. This can be multiple lines of text, and should fully identify the location of the address within its second administrative level (typically a city or town), but should not include the city name, ZIP or postal code, or country name.
- "
shipping" -
The street address to send the product. This can be combined with other tokens, such as "
shipping street-address" and "shipping address-level2". - "
billing" -
The street address to associate with the form of payment used. This can be combined with other tokens, such as "
billing street-address" and "billing address-level2". - "
address-line1", "address-line2", "address-line3" -
Each individual line of the street address. These should only be present if the "
street-address" is not present. - "
address-level4" -
The finest-grained administrative level, in addresses which have four levels.
- "
address-level3" -
The third administrative level, in addresses with at least three administrative levels.
- "
address-level2" -
The second administrative level, in addresses with at least two of them. In countries with two administrative levels, this would typically be the city, town, village, or other locality in which the address is located.
- "
address-level1" -
The first administrative level in the address. This is typically the province in which the address is located. In the United States, this would be the state. In Switzerland, the canton. In the United Kingdom, the post town.
- "
country" -
A country or territory code.
- "
country-name" -
A country or territory name.
- "
postal-code" -
A postal code (in the United States, this is the ZIP code).
- "
cc-name" -
The full name as printed on or associated with a payment instrument such as a credit card. Using a full name field is preferred, typically, over breaking the name into pieces.
- "
cc-given-name" -
A given (first) name as given on a payment instrument like a credit card.
- "
cc-additional-name" -
A middle name as given on a payment instrument or credit card.
- "
cc-family-name" -
A family name, as given on a credit card.
- "
cc-number" -
A credit card number or other number identifying a payment method, such as an account number.
- "
cc-exp" -
A payment method expiration date, typically in the form "MM/YY" or "MM/YYYY".
- "
cc-exp-month" -
The month in which the payment method expires.
- "
cc-exp-year" -
The year in which the payment method expires.
- "
cc-csc" -
The security code for the payment instrument; on credit cards, this is the 3-digit verification number on the back of the card.
- "
cc-type" -
The type of payment instrument (such as "Visa" or "Master Card").
- "
transaction-currency" -
The currency in which the transaction is to take place.
- "
transaction-amount" -
The amount, given in the currency specified by "
transaction-currency", of the transaction, for a payment form. - "
language" -
A preferred language, given as a valid BCP 47 language tag.
- "
bday" -
A birth date, as a full date.
- "
bday-day" -
The day of the month of a birth date.
- "
bday-month" -
The month of the year of a birth date.
- "
bday-year" -
The year of a birth date.
- "
sex" -
A gender identity (such as "Female", "Fa'afafine", "Hijra", "Male", "Nonbinary"), as freeform text without newlines.
- "
tel" -
A full telephone number, including the country code. If you need to break the phone number up into its components, you can use these values for those fields:
- "
tel-country-code" -
The country code, such as "1" for the United States, Canada, and other areas in North America and parts of the Caribbean.
- "
tel-national" -
The entire phone number without the country code component, including a country-internal prefix. For the phone number "1-855-555-6502", this field's value would be "855-555-6502".
- "
tel-area-code" -
The area code, with any country-internal prefix applied if appropriate.
- "
tel-local" -
The phone number without the country or area code. This can be split further into two parts, for phone numbers which have an exchange number and then a number within the exchange. For the phone number "555-6502", use "
tel-local-prefix" for "555" and "tel-local-suffix" for "6502". - "
tel-extension" -
A telephone extension code within the phone number, such as a room or suite number in a hotel or an office extension in a company.
- "
impp" -
A URL for an instant messaging protocol endpoint, such as "xmpp:username@example.net".
- "
url" -
A URL, such as a home page or company website address as appropriate given the context of the other fields in the form.
- "
photo" -
The URL of an image representing the person, company, or contact information given in the other fields in the form.
- "
webauthn" -
Passkeys generated by the Web Authentication API, as requested by a conditional
navigator.credentials.get()call (i.e., one that includesmediation: 'conditional'). See Sign in with a passkey through form autofill for more details.
type-attributtet
På mobil vil skjermtastaturet velges ut fra verdien på type-attributtet til input-tag'en. Dette gjelder spesielt for: email, number, search, tel, text og url.
Vanligvis skal du bruke type-attributtet så riktig tastatur velges, men for noen felt innebærer dette validering fra nettleseren. Skriv for eksempel inn en epost-adresse med feil format i tilbakemeldingsskjemaet på dette nettstedet og sjekk hva som skjer. I tillegg til validering vil type-attributtet kunne legge til kontroller. For number får du eksempelvis ofte pil opp/ned for å endre verdi, og det er ikke alltid det du ønsker (se eksempel helt nederst i artikkelen).
inputmode-attributtet
inputmode brukes for å bestemme hvilket skjermtastatur som skal vises, altså litt overlappende med type-attributtet. inputmode vil derimot ikke føre til nettleser-validering av at det som skrives i et felt er syntaktisk riktig.
inputmode-verdier
- none
- Ikke noe virtuelt tastatur. Siden implementerer sin egen tastaturkontroll.
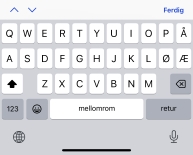
- text (standardverdi)
- Standardtastaturet for tekst benyttes.
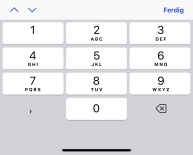
- decimal
- Numerisk tastatur som inneholder sifrene og desimalskilletegn (vanligvis . eller ,
).
Enheter viser kanskje en minustast (-).
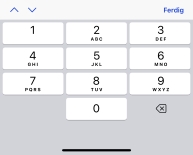
- numeric
- Numerisk tastatur (sifrene 0–9). Enheter kan vise en minustast eller ikke.
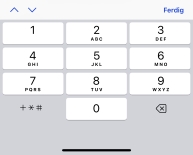
- tel
- Nummeriske taster, * og #. Felt som skal inneholde telefonnummer skal vanligvis
bruke
type="tel":
<input type="tel">
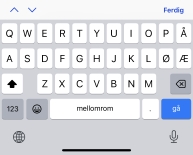
- search
- Et virtuelt tastatur optimalisert for søk For eksempel retur/send-knapp (kan være
merket
"Søk"), sammen med mulige andre optimaliseringer. Inndata som krever et søk bør
vanligvis bruke:
<input type="search">
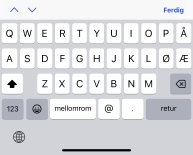
- Et virtuelt tastatur optimalisert for å legge inn e-postadresser. Inkluderer
vanligvis "@"
og ".". Inndata som krever e-postadresser skal vanligvis bruke:
<input type="email">
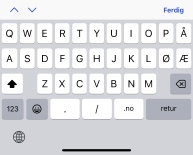
- url
- Et tastatur som er optimalisert for å legge inn nettadresser med for eksempel "/".
Felt som
skal fylles ut med url skal vanligvis bruke:
<input type="url">
Type eller inputmode?
type og inputmode brukes altså for å bestemme skjermtastaturet på mobile enheter. Som nevnt over har imidlertid attributtene litt ulike bruksområder (selv om mange attributtverdier er identiske):
- type
- Definerer typen av datafeltet, som tekst, e-post, tall, osv., og instruerer nettleseren om hvilken type data som forventes. Nettleseren velger automatisk et passende tastatur basert på datatypen. Bruk av type kan medføre validering fra nettleseren.
- inputmode
- Bestemmer hvilket skjermtastatur som skal brukes, uavhengig av datatypen. Nyttig når standardtastaturet for en gitt "type" ikke er optimalt.
type er vanligvis det du skal benytte, men med inputmode som et ekstra attributt dersom type ikke
velger det best egnede tastaturet. I et tekstfelt der du forventer et tall kan du for
eksempel bruke inputmode="numeric"